Strengthening Cyber Security with the Principle of Least Privilege
May 28, 2024

In cybersecurity, the principle of least privilege (PoLP) stands as a fundamental concept for safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating the risks of unauthorized access. This principle revolves around the idea of restricting access rights for users, systems, and processes to only the bare minimum permissions necessary to perform their tasks. By adhering to the principle of least privilege, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture and reduce the likelihood of data breaches and insider threats.
Understanding the Principle of Least Privilege
At its core, the principle of least privilege operates on the principle of minimization – minimizing the potential impact of a security breach by limiting the access privileges granted to users or systems. Rather than providing broad, unrestricted access to resources, the principle advocates for granting individuals or processes only the permissions required to carry out their specific functions.
Key Benefits of Implementing Least Privilege
- Limiting Exposure to Cyber Threats: By restricting access rights, organizations can minimize the attack surface available to malicious actors. Even if a user account is compromised, the limited privileges reduce the potential damage that an attacker can inflict.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: The principle of least privilege ensures that users can only access the resources necessary for their roles and responsibilities. This helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data or critical systems, thereby enhancing overall data security.
- Mitigating Insider Threats: Insider threats, whether intentional or accidental, pose a significant risk to organizations. By implementing least privilege, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with insider threats by limiting the potential damage that insiders can cause through unauthorized access or malicious actions.
- Enhancing Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Many regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR and HIPAA, require organizations to implement adequate access controls and data protection measures. Adhering to the principle of least privilege helps organizations demonstrate compliance with these regulations by ensuring that access to sensitive data is appropriately restricted.
Best Practices for Implementing Least Privilege
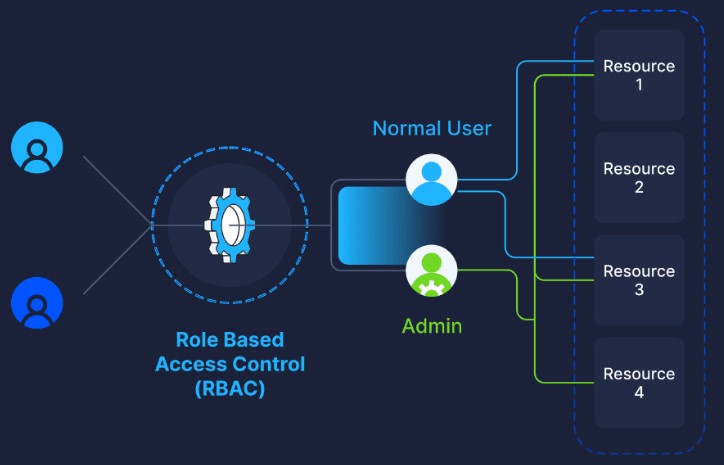
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to assign permissions based on users’ roles and responsibilities within the organization. This ensures that users only have access to the resources necessary to fulfill their job functions.
- Regular Access Reviews: Conduct regular access reviews to identify and revoke unnecessary permissions granted to users over time. This helps prevent access creep and ensures that access rights remain aligned with users’ current roles and responsibilities.
- Use of Privileged Access Management (PAM) Solutions: Leverage PAM solutions to manage and monitor privileged accounts and access to critical systems. PAM solutions help enforce least privilege by controlling and auditing privileged access to sensitive resources.
- Educate Users: Educate users about the importance of least privilege and the potential risks associated with excessive access rights. Encourage users to report any suspicious activities or access requests that may indicate unauthorized access attempts.
In today’s threat landscape, implementing the principle of least privilege is essential for maintaining robust cybersecurity defenses. By limiting access rights and adhering to the principle of least privilege, organizations can reduce their exposure to cyber threats, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate the risks of insider threats. By embracing least privilege as a foundational security principle, organizations can strengthen their security posture and safeguard their sensitive data and critical assets against potential security breaches.

Have Any Question?
Call or email Cocha. We can help with your cybersecurity needs!
- (281) 607-0616
- info@cochatechnology.com