Botnet and Botnet Attacks
May 12, 2023
Botnets have become a significant threat to cybersecurity in recent years. These malicious networks of infected computers, or “bots,” can be used to carry out a wide range of attacks, including distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, spamming, phishing, and even cryptocurrency mining. In this blog post, we will explore what botnet attacks are, how they work, and what steps you can take to avoid falling victim to them.
What is a Botnet Attack?
A botnet attack is a type of cyber attack where a network of compromised computers is used to carry out malicious activities. These networks can range in size from a few hundred to millions of devices. The attacker can use these botnets to launch DDoS attacks, spread malware, steal sensitive information, and even control the infected computers remotely.
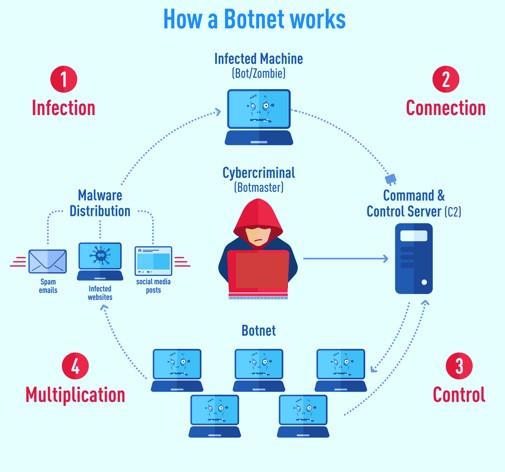
How Do Botnet Attacks Work?
Botnets work by infecting computers with malware that allows the attacker to take control of the device. The malware can be spread in a variety of ways, such as phishing emails, drive-by downloads, or malicious downloads from infected websites.
Once the malware infects a device, it will connect to a command-and-control (C&C) server operated by the attacker. This server is used to issue commands to the infected devices, allowing the attacker to control them remotely. These commands can be used to carry out a wide range of malicious activities, such as launching DDoS attacks or stealing sensitive information.
How to Avoid Botnet Attacks
Keep Your Software Up-to-Date: One of the most effective ways to avoid botnet attacks is to keep your software up-to-date. This includes not only your operating system but also your web browser, email client, and any other software installed on your computer. Updates often include security patches that fix known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Use Antivirus Software: Antivirus software can detect and remove malware before it has a chance to infect your computer. Make sure to keep your antivirus software up-to-date and run regular scans to ensure that your computer is not infected.
Be Careful What You Click: Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. This includes email attachments, links in instant messages, and links on social media. Even if the message appears to be from a trusted source, be cautious and verify the link or attachment before clicking on it.
Use Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts. This means that even if an attacker manages to steal your password, they will still need to provide an additional form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone.
Always be vigilant and stay informed about the latest threats and best practices for cybersecurity to stay safe online.
Have Any Question?
Call or email Cocha. We can help with your cybersecurity needs!
- (281) 607-0616
- info@cochatechnology.com